A hybrid turbocharger is an electric turbocharger consisting of an ultra high speed turbine-generator and an ultra high speed electric aircompressor. The turbine and compressor are high-speed aeromachines, as in a conventional turbocharger. The electrical motors run at speeds in excess of 120,000 rpm and when used as generators, generate electricity at up to 98.5% electrical efficiency. High electrical efficiency is paramount, because there is no mechanical link between the turbine and compressor. In other words, hybrid turbocharger refers to a series hybridsetup, in which compressor speed and power are independent from turbine speed and power. This design flexibility leads to further improvements in turbine and compressor efficiency, beyond a conventional turbocharger.
The designers claim that hybrid turbocharger technology (HTT) virtually eliminates turbo lag and enables engine downsizing without compromising engine performance. This means that a HTT equipped engine can save up to 30% on CO2 emissions and fuel economy compared to an equivalent naturally aspirated engine.
Physical arrangement
The electric motors utilize permanent magnets which have a higher efficiency than standard high speed induction motors. Induction motors induce an electro-magnetic field into a solid rotor core. The induction motor is much simpler to control, but there are substantial losses involved in generating the magnetic field in the rotor.
The HTT motor will accelerate from 40,000 to 120,000 rpm in less than 450 ms. The HTT motor control therefore requires a fast acting CPU to match the magnetic field of the stator to the changing position of the roto
Acceleration
When the driver depresses the throttle, the HTT initially acts like an electric supercharger. The compressor motor is powered from the energy storage medium allowing it to accelerate to full operating speed in <500 ms. This rate of acceleration eliminates the turbo lag which is a major limiting factor on the performance of standard turbocharged engines.
During this transient stage, the engine control unit (ECU) on a standard turbocharged engine uses a combination of sensors such as lambda sensors and air mass flow sensors to regulate the fuel flow rate. In an HTT equipped engine the ECU can deliver the precise fuel flow rate for complete combustion more accurately. This is achieved by directly controlling the air flow rate and boost pressure via control of the compressor speed.
Aeristech's prototype motor delivers 26 kW (35 PS; 35 hp) at 120,000 rpm, weighs under 3.5 kg (8 lb) and is approximately 10 centimetres (4 in) in length.
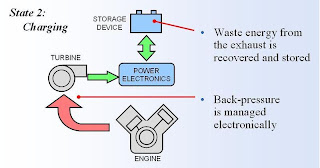
Charging
At high engine speeds there is more energy generated by the turbine than is required by the compressor. Under these conditions, the excess energy can be used to recharge the energy storage for the next acceleration phase or used to power some of the auxiliary loads such as an electric air conditioning system.
When combined with a variable geometry turbine, the back pressure on the engine can be varied according to the electrical demands of the vehicle and charge state of the energy storage medium.
Development is underway for replacing battery energy storage with a super capacitor which can be charged and discharged very quickly
System benefits
Aeristech claim many other benefits to running a hybrid turbocharged engine:
- Improved packaging by enabling the turbine and compressor to be placed in separate parts of the engine bay.
- Higher density charge air by reducing the length of intake ducts and increasing the size of the compressor wheel.
- ECU controlled boost levels will enable tighter predictive control of in-cylinder combustion.
- Similar engine downsizing benefits to a hybrid vehicle, but with far less (approx 1/7th) energy storage capacity to achieve the same level of downsizing.
Other types of electric turbochargers and electric superchargers are under development with varying degrees of success:
- eBooster by BorgWarner - a small auxiliary electric compressor powered by the vehicle's electric system.
- TurboPac by TurboDyne - Electric supercharger
- Garrett electrically-assisted turbo
- Valeo - Electric supercharger using a low-inertia switched-reluctance motor












0 comments:
Post a Comment